Alabama, a state of the southeastern United States, between the Cumberland Mountains in the north and the Gulf of Mexico in the south. Border to Mississippi in the west, Tennessee in the north, Georgia in the east, and to the south, Alabama borders Florida and the Gulf of Mexico – with a coastline of approx. 85 km. The state is abbreviated Ala. or AL, and is also referred to as the Heart of Dixie or Camellia State. The name Alabama comes from choctaw alba almoh, the “scrub grower“.
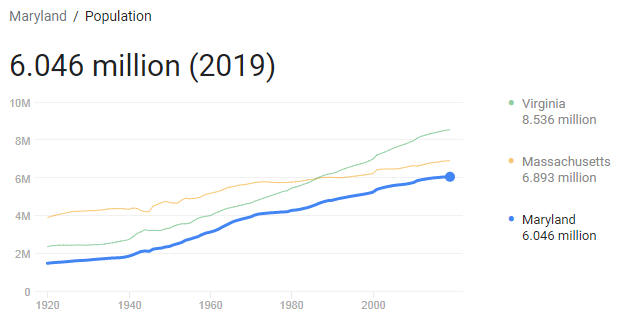
Alabama has a total area of approx. 135,760 km2, and has 4,874,747 residents (US Census, 2017). Alabama was listed as the 22nd state of the United States on December 14, 1819. The capital is Montgomery, and the largest city is Birmingham. See cities in Alabama.
Geography
Alabama can be divided into two equally large geographical areas. The northern part belongs to the Appalachians and is intersected by the Tennessee River. The landscape is characterized by folding mountains, with Cheaha Mountain (734 masl) as the highest point. The southern part forms a fertile coastal plain with black soil and wooded sandy moors farthest off the coast. The climate is temperate to subtropical, with a long growing season, approx. 300 days in the south and approx. 200 in the north.
Population
69.2 percent of the population is considered white – including 4.3 percent Hispanic (Hispanic or Latino) – while 26.8 percent are African American (US Census, 2017). About 59 percent of the population lives in cities. The highest population density is in the Black Belt area. The largest cities in the state are the iron and steel center Birmingham with 210 710 residents, the capital Montgomery with 199 518 residents, Huntsville with 194 585 residents and the port city of Mobile with 190 265 residents (US Census, 2017). The largest church community in Alabama is the Baptist community.
Business
Despite the rapid industrialization, agriculture is considerable. Traditionally it has concentrated on cotton cultivation, but the production of maize, soybeans, pecans and peanuts is becoming increasingly important, followed by potatoes, melons, tobacco and peaches. Animal husbandry places particular emphasis on the production of poultry (broilers) and egg production. Two-thirds of the area is wooded, mostly with pine, which provides the basis for a significant timber processing industry.
The hydropower development in the Tennessee Valley has created the basis for strong industrial growth, with aluminum, textile and chemical industries. In addition, three major nuclear power plants have been built in the northern part of the state. At Huntsville in the north, in the 1950s, Wernher von Braun built a space center, the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center, which is still one of the leading in the country. The deposits of coal, iron ore, bauxite, natural gas and oil have also helped make Alabama the leading heavy industrial state in the south. US Steel in Birmingham has been the key company.
Alabama elects two senators and seven members of Congress.
History
Alabama was explored by the Spaniards in the early 16th century. The area gained its first permanent settlement by the French in 1702 (Fort Louis), and belonged to French Louisiana until 1763, British 1763–83. The Mobile Bay area remained under Spanish control until it came under American control in 1813. Alabama was organized as territory in 1817 and occupied as the 22nd state in the Union on December 14, 1819. Alabama withdrew from the Union during the American Civil War in 1861 and joined the Southern State Confederation which for a time had Montgomery as its capital.